Budget Elements: Your Blueprint for Smart Money Management
When working with budget elements, the individual components that make up a personal budgeting system—income, expense categories, savings goals, and cash‑flow buckets. Also known as budget components, it gives you a clear picture of where money comes from and where it goes. Another core piece is budget priorities, the hierarchy of spending that starts with essential bills, then emergency savings, then debt repayment or extra goals, and the emergency fund, a safety‑net of liquid cash for unexpected expenses. Together these ideas form the foundation of any solid financial plan.
How to Use Budget Elements Effectively
Budget elements encompass income streams, expense categories, and savings targets, creating a framework that lets you track cash flow in real time. Effective budgeting requires monitoring cash flow and setting clear financial goals; without that, the numbers become just a list of numbers. An emergency fund influences the stability of a budget because it cushions shocks and prevents the need to tap high‑interest credit. By aligning budget priorities with your long‑term goals, you can allocate the right amount to each element, keep spending realistic, and reserve space for future investments. The 3 R’s—Reality, Reserve, Review—live inside this structure, encouraging you to test your assumptions, set a reserve for surprises, and regularly tweak the plan.
Below you’ll find a curated collection of articles that dive deeper into each of these pieces. Whether you need a quick guide on setting up a basic budget, tips for building an emergency fund, or strategies to review and refine your spending each month, the posts are organized to give you practical steps you can apply today. Use them as a toolbox to sharpen your budgeting skills and keep your finances humming.
5 Essential Elements Every Budget Needs
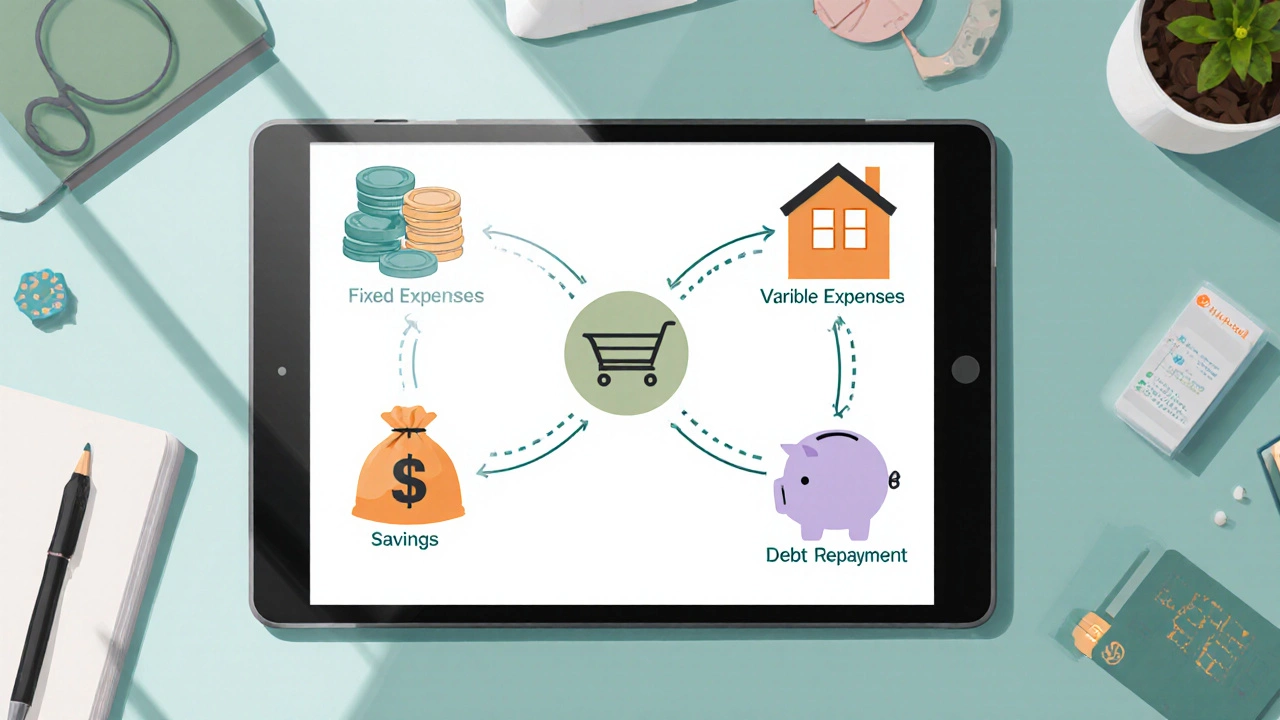
Learn the five fundamental parts of any budget-income, fixed and variable expenses, savings, and debt repayment-and how to use them for real financial control.
Read More >>